

The gray arrows pointing away from each other represent repulsionīecause each end of a dipole possesses only a fraction of the charge of an electron, dipole–dipole interactions are substantially weaker than the interactions between two ions, each of which has a charge of at least ☑, or between a dipole and an ion, in which one of the species has at least a full positive or negative charge. (CC BY-SA-NC anonymous) The green arrows pointing towards each other represent attraction. IOS Press.\): Both attractive and repulsive dipole–dipole interactions occur in a liquid sample with many molecules.

"Computational Aspects of Electric Polarizability Calculations: Atoms, Molecules and Clusters". ^ a b c d e f g h Anslyn, Eric Dougherty, Dennis (2006). The dipole moment ( ) is defined as the product of the magnitude of the charge, e, and the distance separating the positive and negative charges, l: el.
#Molecular dipole moment definition free#
Solivérez, Electrostatics and Magnetostatics of Polarized Ellipsoidal Bodies: The Depolarization Tensor Method, Free Scientific Information, 2016 (2nd edition), ISBN 974-0-3, pp. ^ Electrodynamics of Continuous Media, L.D.Let the charges on the plates be +qand qand their areas are A. Figure 1: Scheme of a charged capacitor without (a) and with (b) dielectric. Molecular dipoles exist if one or more of the atoms is more electronegative than the other(s) The most common dipole is water. Consider two plane, parallel plates depicted in Fig. ^ Atkins, Peter de Paula, Julio (2010). The dipole moment of a molecule may be obtained from measurements of the relative permittivity of a bulk sample.Griffiths, Pearson Education, Dorling Kindersley, 2007, ISBN 81-7758-293-3 ^ Introduction to Electrodynamics (3rd Edition), D.J.
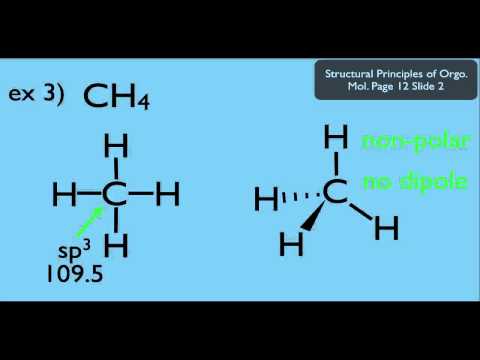
European Organization for Nuclear Research ( CERN). define important terms, such as dipole moment and intermolecular force. "Magnetic polarizability of hadrons particles from lattice QCD" (PDF). Is Good Molecules a Clean Brandquestion 1 of 3 A molecule is defined as a group. The magnetic dipole moment induced in the SRR can be adjusted to be either in or out of phase with the external oscillating field, leading to either a positive or a negative magnetic permeability. The CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. p, molecular dipole moment, k Boltzmann's constant, M molecular. MOSCED, an estimation method for activity coefficients which uses polarizability as one of its parameters Name Symbol Definition Significance Field of Use K VIV ( see Alfven No.Additional tensors composed of products of three or more spin matrices are needed only for the exhaustive description of polarization of particles/nuclei with spin S ≥ 3⁄ 2. This discrepancy is taken into account by the Clausius–Mossotti relation (below) which connects the bulk behaviour ( polarization density due to an external electric field according to the electric susceptibility χ = ε r − 1 and the polarization tensor P `. If the net charge is zero, test for presence of a dipole: If you can draw a line through the molecule such that more negative partial charges are on one side of the line and more positive partial charges are on the other side of the line, it has a dipole moment. Note that the local electric field seen by a molecule is generally different from the macroscopic electric field that would be measured externally. The polarizability of an atom or molecule is defined as the ratio of its induced dipole moment to the local electric field in a crystalline solid, one considers the dipole moment per unit cell. If a molecule contains polar bonds that are unevenly distributed about the center, there will be an uneven charge distribution. Polarizability is responsible for a material's dielectric constant and, at high (optical) frequencies, its refractive index. A dipole moment is simply the measure of net polarity in a molecule. Boron trichloride (BCl3), and boron trifluoride (BF3) are the tetratomic compound having dipole moment zero, indicating that they have a regular planar. When subject to an electric field, the negatively charged electrons and positively charged atomic nuclei are subject to opposite forces and undergo charge separation. It is a property of all matter, considering that matter is made up of elementary particles which have an electric charge, namely protons and electrons. Polarizability usually refers to the tendency of matter, when subjected to an electric field, to acquire an electric dipole moment in proportion to that applied field. For other uses, see Polarization (disambiguation). For electromagnetic waves, see Polarization (waves).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
